04.异步编程
异步编程
同步与异步
分布式网络系统中,各个参与方节点的运行是相互独立的,没有共享内存,没有全局时钟。各节点通过消息来进行沟通。在传统的理念中,我们会把这样的网络根据他们通信方式描述成同步和异步的。
-
同步(Synchronous)就是整个处理过程顺序执行,当各个过程都执行完毕,并返回结果。是一种线性执行的方式,执行的流程不能跨越。一般用于流程性比较强的程序,比如用户登录,需要对用户验证完成后才能登录系统。在 CPU 处理中,表现为处理器等待,直到阻塞调用完成其任务并返回结果。之后,处理器将继续处理下一个任务。这有时可能会引起问题,因为可能无法有效利用 CPU。它可能会等待很长时间。
-
异步(Asynchronous)则是只是发送了调用的指令,调用者无需等待被调用的方法完全执行完毕;而是继续执行下面的流程。是一种并行处理的方式,不必等待一个程序执行完,可以执行其它的任务,比如页面数据加载过程,不需要等所有数据获取后再显示页面。在 CPU 处理中,当异步处理任务时,在同步情况下等待所花费的 CPU 时间改为使用抢占式时间共享算法来处理其他任务。也就是说,不是等待,而是处理其他任务。因此,只要有更多工作可以完成,处理器就永远不会等待。
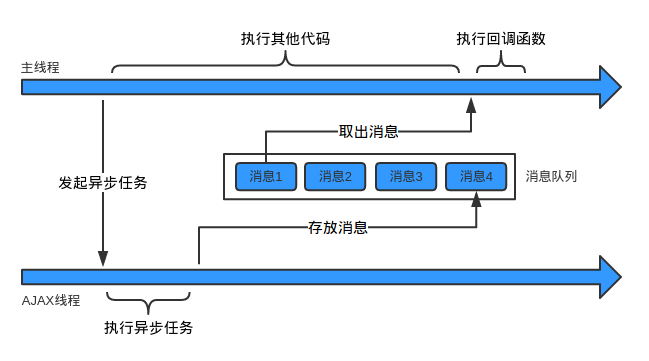
传统的同步编程是一种请求响应模型,调用一个方法,等待其响应返回.。而异步编程就是,发出一个任务,不等待结果,就继续发出下一个任务。至于上一个任务的执行结果,我们可以通过两种方式获得,一个是主动轮询,另一个是单独开一个线程去等待结果接收并回调执行。
异步编程范式
简单的同步数据读取的写法如下:
public class MyClass
{
public int Read(byte [] buffer, int offset, int count);
}
.NET provides three patterns for performing asynchronous operations:
- Task-based Asynchronous Pattern (TAP), which uses a single method to represent the initiation and completion of an asynchronous operation. TAP was introduced in the .NET Framework 4. It’s the recommended approach to asynchronous programming in .NET. The async and await keywords in C# and the Async and Await operators in Visual Basic add language support for TAP. For more information, see Task-based Asynchronous Pattern (TAP).
public class MyClass
{
public Task<int> ReadAsync(byte [] buffer, int offset, int count);
}
- Event-based Asynchronous Pattern (EAP), which is the event-based legacy model for providing asynchronous behavior. It requires a method that has the
Asyncsuffix and one or more events, event handler delegate types, andEventArg-derived types. EAP was introduced in the .NET Framework 2.0. It’s no longer recommended for new development. For more information, see Event-based Asynchronous Pattern (EAP).
public class MyClass
{
public void ReadAsync(byte [] buffer, int offset, int count);
public event ReadCompletedEventHandler ReadCompleted;
}
- Asynchronous Programming Model (APM) pattern (also called the xref:System.IAsyncResult pattern), which is the legacy model that uses the xref:System.IAsyncResult interface to provide asynchronous behavior. In this pattern, synchronous operations require
BeginandEndmethods (for example,BeginWriteandEndWriteto implement an asynchronous write operation). This pattern is no longer recommended for new development. For more information, see Asynchronous Programming Model (APM).
public class MyClass
{
public IAsyncResult BeginRead(
byte [] buffer, int offset, int count,
AsyncCallback callback, object state);
public int EndRead(IAsyncResult asyncResult);
}
