39-实战Kaggle竞赛:CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
1.目录
首先,导入竞赛所需要的包和模块:
import collections
import math
import os
import shutil
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
2.1 下载数据集:
#@save
d2l.DATA_HUB['cifar10_tiny'] = (d2l.DATA_URL + 'kaggle_cifar10_tiny.zip',
'2068874e4b9a9f0fb07ebe0ad2b29754449ccacd')
# 如果你使用完整的Kaggle竞赛的数据集,设置demo为False
demo = True
if demo:
data_dir = d2l.download_extract('cifar10_tiny')
else:
data_dir = '../data/cifar-10/'
为了便于入门,我们提供包含前 1000 个训练图像和 5 个随机测试图像的数据集的小规模样本,如果要获取完整数据集,你需要将一下 demo 变量设置为 False
2.2 整理数据集
首先我们用以下函数读取 CSV 文件中的标签,它返回一个字典,该字典将文件名中不带拓展名德部分映射到其标签。
def read_csv_labels(fname):
"""读取fname来给标签字典返回一个文件名"""
with open(fname, 'r') as f:
# 跳过文件头行(列名)
lines = f.readlines()[1:]
tokens = [
# 训练样本 : 1000l.rstrip().split(',') for l in lines]
return dict(((name, label) for name, label in tokens))
labels = read_csv_labels(os.path.join(data_dir, 'trainLabels.csv'))
print('# 训练样本 :', len(labels))
print('# 类别 :', len(set(labels.values())))
# 训练样本 : 1000
# 类别 : 10
接下来,我们定义 reorg_train_valid 函数来将验证集从原始的训练集中拆分出来。此函数中的参数 valid_ratio 是验证集中的样本数与原始训练集中的样本数之比。更具体的说,令 n 等于样本最少的类别中的图像数量,而 r 是比率。验证集将为每个类别拆分出 max([nr],1)张图像。让我们以 valid_ratio=0.1 为例,由于原始的训练集有 50000 张图像,因此 trian_valid_test/train 路径中将有 45000 张图像用于训练,而剩下 5000 张图像将作为路径 train_valid_test/valid 中的验证集。组织数据集后,同类别的图像将被放置在同一文件夹下。
def copyfile(filename, target_dir):
"""将文件复制到目标目录"""
os.makedirs(target_dir, exist_ok=True)
shutil.copy(filename, target_dir)
#@save
def reorg_train_valid(data_dir, labels, valid_ratio):
"""将验证集从原始的训练集中拆分出来"""
# 训练数据集中样本最少的类别中的样本数
n = collections.Counter(labels.values()).most_common()[-1][1]
# 验证集中每个类别的样本数
n_valid_per_label = max(1, math.floor(n * valid_ratio))
label_count = {}
for train_file in os.listdir(os.path.join(data_dir, 'train')):
label = labels[train_file.split('.')[0]]
fname = os.path.join(data_dir, 'train', train_file)
copyfile(fname, os.path.join(data_dir, 'train_valid_test',
'train_valid', label))
if label not in label_count or label_count[label] < n_valid_per_label:
copyfile(fname, os.path.join(data_dir, 'train_valid_test',
'valid', label))
label_count[label] = label_count.get(label, 0) + 1
else:
copyfile(fname, os.path.join(data_dir, 'train_valid_test',
'train', label))
return n_valid_per_label
其中 os.listdir 显示指定路径下的文件和文件夹列表
下面的 reorg_test 函数用来预测期间整理测试集,以方便读取。
#@save
def reorg_test(data_dir):
"""在预测期间整理测试集,以方便读取"""
for test_file in os.listdir(os.path.join(data_dir, 'test')):
copyfile(os.path.join(data_dir, 'test', test_file),
os.path.join(data_dir, 'train_valid_test', 'test',
'unknown'))
最后我们使用一个函数来调用前面定义的函数 read_csv_labels,reorg_train_valid 和 reorg_test。
def reorg_cifar10_data(data_dir, valid_ratio):
labels = read_csv_labels(os.path.join(data_dir, 'trainLabels.csv'))
reorg_train_valid(data_dir, labels, valid_ratio)
reorg_test(data_dir)
在这里,我们只将样本数据集的批量大小设置为 32.在实际训练和测试中,应该使用 Kaggle 竞赛的完整数据集,并将 batch_size 设置为更大的整数,例如 128.我们将 10%的训练样本作为调整超参数的验证集。
batch_size = 32 if demo else 128
valid_ratio = 0.1
reorg_cifar10_data(data_dir, valid_ratio)
3.图像增广
使用图像增广来解决过拟合问题。在训练中,我们可以随机水平翻转图像。我们可以对彩色图像的三个 RGB 通道执行标准化。下面为一些可以调整的操作
transform_train = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
# 在高度和宽度上将图像放大到40像素的正方形
torchvision.transforms.Resize(40),
# 随机裁剪出一个高度和宽度均为40像素的正方形图像,
# 生成一个面积为原始图像面积0.64到1倍的小正方形,
# 然后将其缩放为高度和宽度均为32像素的正方形
torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(32, scale=(0.64, 1.0),
ratio=(1.0, 1.0)),
torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
# 标准化图像的每个通道
torchvision.transforms.Normalize([0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465],
[0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010])])
在测试期间,我们只对图像执行标准化,以消除评估结果中的随机性
transform_test = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize([0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465],
[0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010])])
4.读取数据集
读取由原始图像组成的数据集,每个样本都包括一张图片和一个标签。
train_ds, train_valid_ds = [torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(
os.path.join(data_dir, 'train_valid_test', folder),
transform=transform_train) for folder in ['train', 'train_valid']]
valid_ds, test_ds = [torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(
os.path.join(data_dir, 'train_valid_test', folder),
transform=transform_test) for folder in ['valid', 'test']]
当验证集在超参数调整过程中用于模型评估中,不应引入图像增广的随机性。在最终预测之前,我们根据训练集合验证集组合而成的训练模型进行训练,以充分利用所有标记的数据
train_iter, train_valid_iter = [torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
for dataset in (train_ds, train_valid_ds)]
valid_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(valid_ds, batch_size, shuffle=False,
drop_last=True)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size, shuffle=False,
drop_last=False)
5.定义模型
直接使用 Resnet-18 模型
def get_net():
num_classes = 10
net = d2l.resnet18(num_classes, 3)
return net
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction="none")
6.定义训练函数
def train(net, train_iter, valid_iter, num_epochs, lr, wd, devices, lr_period,
lr_decay):
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr, momentum=0.9,
weight_decay=wd)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(trainer, lr_period, lr_decay)
num_batches, timer = len(train_iter), d2l.Timer()
legend = ['train loss', 'train acc']
if valid_iter is not None:
legend.append('valid acc')
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],
legend=legend)
net = nn.DataParallel(net, device_ids=devices).to(devices[0])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
net.train()
metric = d2l.Accumulator(3)
for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
l, acc = d2l.train_batch_ch13(net, features, labels,
loss, trainer, devices)
metric.add(l, acc, labels.shape[0])
timer.stop()
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,
(metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[2],
None))
if valid_iter is not None:
valid_acc = d2l.evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, valid_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, valid_acc))
scheduler.step()
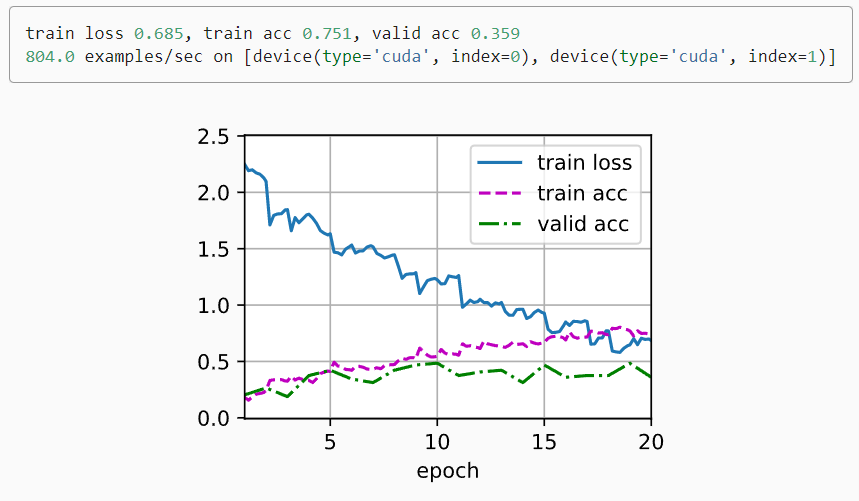
measures = (f'train loss {metric[0] / metric[2]:.3f}, '
f'train acc {metric[1] / metric[2]:.3f}')
if valid_iter is not None:
measures += f', valid acc {valid_acc:.3f}'
print(measures + f'\n{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f}'
f' examples/sec on {str(devices)}')
使用随机梯度下降和学习率规划来训练模型,以更快达到收敛。
7.训练和验证模型
以下所有超参数都可以调节
devices, num_epochs, lr, wd = d2l.try_all_gpus(), 20, 2e-4, 5e-4
lr_period, lr_decay, net = 4, 0.9, get_net()
train(net, train_iter, valid_iter, num_epochs, lr, wd, devices, lr_period,
lr_decay)
8.Q&A
Q1:深度学习的损失函数一般是非凸的吗?
损失函数一般是凸的,但是神经网络是非凸的(非单层)。凸函数表示能力有限。
Q2:训练时的训练集交叉熵 loss 大于验证集,但是训练集 acc 也是大于验证集的?
应该是因为在训练集上加了数据增广
Q3:normalize 参数怎么来的?
由 imagenet 数据集上 RGB 的均值和方差
Q4:weight decay 和 lr decay 的作用有什么区别吗?
weight decay 是对权重更新的操作——正则化(统计),lr decay 是作用在学习率上——为了收敛(优化模型)
Q5:scheduler 怎么设置是最好的最优的,怎么选择?
现在一般选用 cosine 函数,参数设置较少 。最好在前期保证比较大的 lr,后期 lr 可以变小一点。具体流行什么说不准
Q6:lr decay 和 weight decay 的效果?
效果类似,但是本质不同。
