会员系统 DSL 描述
会员系统 DSL 描述
如花是一名架构师,对 DDD 也非常熟悉,而且有过几个项目的 DDD 实践,最近他加入会员线,负责完成对会员系统的改造,更好地配合公司的微服务化的设计思路。会员线之前就是三个应用:会员中心对外提供的大量的 REST API 服务;会员注册和登录应用;会员中心,处理会员登录后如修改个人密码、基本信息、SNS 第三方绑定和支付方式绑定等。
如花加入会员团队后,和大家沟通了基于 DDD + MicroServices 的架构思想,大家都表示同意,但是如何落实到具体的架构设计和文档上,大家就犯难啦。
从 SubDomain 开始
如花开始 DDD 的第一步,也就是 Subdomain 的划分;如花首先将会员先划分为几个 Sub Domain,如处理账号相关的 Account,处理会员打标的 UserTag,处理支付方式的 PaymentProfile,处理社交平台集成的 SnsProfile,还有一个其他 Profiles,这里我们不涉及 Generic 和 Supporting Doman 的规划,主要从业务核心 Domain 出发。一个同学用 PPT 阐述了划分结构和出发点,如下:
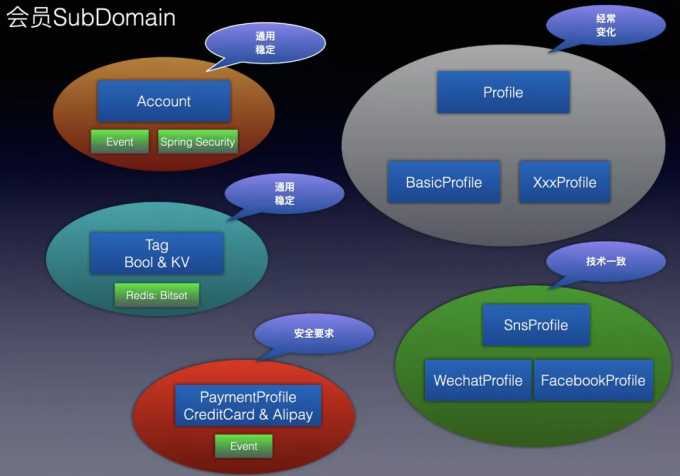
UML 图如下:
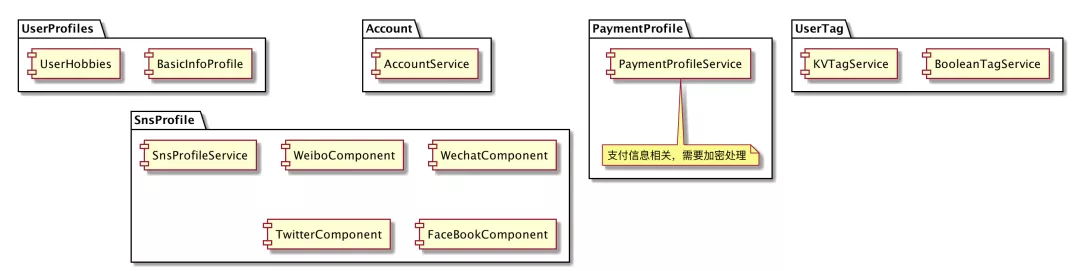
DDD 的第一步:SubDomain 的划分和展现,就有不同的理解方式,如何描述、如何图形化展现,都有不少的分歧。回到问题的出发点,我们就想划分一下 SubDomain,那么是不是下述的 DSL 代码也可以:
Domain User {
domainVisionStatement = "User domain to manage account, tags, profiles and payment profile."
Subdomain AccountDomain {
type = CORE_DOMAIN
domainVisionStatement = "Account domain to save sensitive data and authentication"
}
Subdomain UserTagDomain {
type = GENERIC_SUBDOMAIN
domainVisionStatement = "UserTag domain manage user's KV and Boolean tag"
}
Subdomain PaymentProfileDomain {
type = CORE_DOMAIN
domainVisionStatement = "User payment profile domain to manage credit/debit card, Alipay payment information"
}
Subdomain SnsProfileDomain {
type = CORE_DOMAIN
domainVisionStatement = "User Sns profile domain to manage user Sns profile for Weibo, Wechat, Facebook and Twitter."
}
Subdomain ProfilesDomain {
type = CORE_DOMAIN
domainVisionStatement = "User profiles domain to manage user basic profile, interest profile etc"
}
}
虽然目前我们还不知道对应的 DSL 代码语法,但是我们已经知道 Domain 的名称、domain 类型以及 domain 的愿景陈述(visionStatement),至于后期以何种方式展现系统 Domain,如表格、图形等,这个可以考虑基于现在的数据进行展现。其中的 UserTagDomain 类型为 GENERIC_SUBDOMAIN,这个表示打标是通用性 Domain,如我们后期可以和商品、图片或者视频团队合作,大家可以一起共建打标系统。
注意,Subdomain 不只是简单包括 type 和 domainVisionStatement,同时你可以添加 Entity 和 Service,其目的主要是突出核心特性并方便你对 Domain 的理解,如 Account 中添加 resetPassword 和 authBySmsCode,相信大多数人都知道这是什么含义。但是注意不要将其他对象添加到 Subdomain,如 VO, Repository, Domain Event 等,这些都是辅助开发的,应该用在 BoundedContext 中。
Subdomain AccountDomain {
type = CORE_DOMAIN
domainVisionStatement = "Account domain to save sensitive data and authentication"
Entity Account {
long id
String nick
String mobile
String ^email
String name
String salt
String passwd
int status
Date createdAt
Date updatedAt
}
Service AccountService {
void updatePassword(long accountId, String oldPassword, String newPassword);
void resetPassword(long acountId);
boolean authByEmail(String email, String password);
boolean authBySmsCode(String mobile, String code);
}
}
Context Map
ContextMap 主要是描述各个 Domain 中各个 BoundedContext 间的关联关系,你可以理解为 BoundedContext 的拓扑地图。这里我们先不详细介绍 BoundedContext,你现在只需要理解为实现 Domain 的载体,如你编写的 HSF 服务应用、一个处理客户请求的 Web 应用或者手机 App,也可以是你租用的一个外部 SaaS 系统等。举一个例子,你的系统中有一个 blog 的 SubDomain,你可以自行开发,也可以架设一个 WordPress,或者用 Medium 实现 Blog。回到微服务的场景,如何划分微服务应用?SubDomain 对应的是业务或者虚拟的领域,而 BoundedContext 则是具体支持 SubDomain 的微服务应用,当然一个 SubDomain 可能对应多个微服务应用。
既然是描述各个 BoundedContext 关系,必然会涉及到关联关系,如 DDD 推荐的 Partnership([P]<->[P])、Shared Kernel([SK]<->[SK])、Customer/Supplier([C]<-[S])、Conformist(D,CF]<-[U,OHS,PL])、Open Host Service、Anticorruption Layer([D,ACL]<-[U,OHS,PL])、Published Language 等,详细的介绍大家可以参考 DDD 图书。这些对应关系都有对应的缩写,就是括号内的表述方法。这里给出关联关系 Cheat Sheet 说明图:
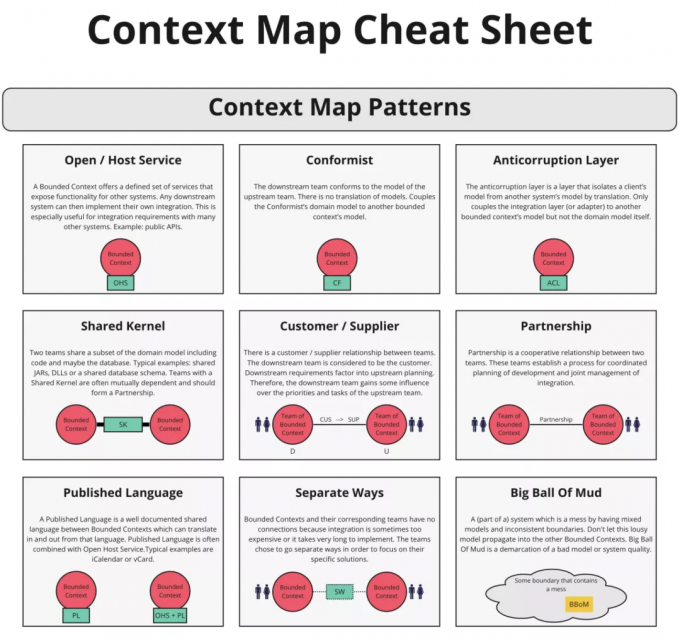
ContextMap UserContextMap {
type = SYSTEM_LANDSCAPE
state = TO_BE
contains AccountContext
contains UserTagContext
contains PaymentProfileContext
contains SnsProfileContext
contains ProfilesContext
contains UserLoginContext
contains UserRegistrationContext
UserLoginContext [D]<-[U] AccountContext {
implementationTechnology = "RSocket"
exposedAggregates = AccountFacadeAggregate
}
ProfilesContext [D]<-[U] UserTagContext {
implementationTechnology = "RSocket"
exposedAggregates = UserTags
}
UserRegistrationContext [D,C]<-[U,S] UserTagContext {
implementationTechnology = "RSocket"
exposedAggregates = UserTags
}
UserRegistrationContext [D,C]<-[U,S] SnsProfileContext {
implementationTechnology = "RSocket"
}
}
大家可以看到 Map 图中包含的各个 BoundedContext 名称,然后描述了它们之间的关系。在关联关系描述中,涉及到对应的描述。前面我们说明 BoundedContext 为 Domain 的具体系统和应用的承载,所以涉及到对应的技术实现。如 HTTP REST API、RPC、Pub/Sub 等,如 blog 系统为 Medium 的话,那么 implementationTechnology = ”REST API"。还有 exposedAggregates,表示暴露的聚合信息,如 class 对象和字段,服务接口等,方便通讯双方做对接,这个我们会在 BoundedContext 中进行介绍。
BoundedContext
在 ContextMap 中我们描述了它们之间的关联关系,接下来我们要进行 BoundedContext 的详细定义。BoundedContext 包含的内容相信大多数同学都知道,如 Entity,ValueObject,Aggregate,Service,Repository、DomainEvent 等,这个大家应该都比较熟悉。这里我们给出一个 ContextMapper 对 BoundedContext 的代码,如下:
BoundedContext AccountContext implements AccountDomain {
type = APPLICATION
domainVisionStatement = "Managing account basic data"
implementationTechnology = "Kotlin, Spring Boot, MySQL, Memcached"
responsibilities = "Account", "Authentication"
Aggregate AccountFacadeAggregate {
ValueObject AccountDTO {
long id
String nick
String name
int status
Date createdAt
def toJson();
}
/* AccountFacade as Application Service */
Service AccountFacade {
@AccountDTO findById(Integer id);
}
}
Aggregate Accounts {
Entity Account {
long id
String nick
String mobile
String ^email
String name
String salt
String passwd
int status
Date createdAt
Date updatedAt
}
}
}
这里对 BoundedContext 再说明一下:
-
BoundedContext 的名称,这个不用说啦,这个和 ContextMap 中名称一致。
-
implements AccountDomain:表示要实现哪一个 SubDomain,我们都知道一个 Subdomain 可能会包含多个 BoundedContext,这些 BoundedContext 配合起来完成 Subdomain 的业务需求。ContextMap 还提供 refines,来表示 BoundedContext 要实现一些 user case,官方文档有对应的说明。
-
BoundedContext 的属性字段:type 表示类型,如 APPLICATION、SYSTEM 等。domainVisionStatement 描述一下 BoundedContext 的职责。implementationTechnology 表示具体的技术,前面我们说到 BoundedContext 已经涉及具体的应用和系统等,所以要说明对应的技术方案实现,核心的部分描述一下就可以。responsibilities 表示 BoundedContext 的职责列表,这里只需要关键字就可以,如 Account 要负责安全验证等。
-
AccountFacadeAggregate: 表示提供给外部调用的聚合,这里 DTO 的对象定义、服务接口的定义等。
-
Aggregate Accounts:这个表示 BoundedContext 内部的聚合,如 entity、value object、service 等。这里说明一下,DDD 中的那个 Aggregate 是 entity,value object 的聚合对象,而 ContextMapper 中的 Aggregate 表示为一些资源的集合,如 Service 集合等。
BoundedContext 的更多信息,可以参考 sculptor 的文档,根据实际的情况可以添加对应的部分,如 DomainEvent、Repository 等。
其它特性
UserStory
这个 DSL 比较明确的,主要是三元素:作为 “aaa",我希望能"xxx",我希望能”yyyy",以便 “zzz”,也是符合 UserStory 的典型三要素:角色、活动和商业价值。
UserStory Customers {
As a "Login User"
I want to update a "Avatar"
I want to update an "Address"
so that "I can manage the personal data."
}
UseCase
Use Case 是描述需求的一种方式,在 UML 图就有对应的 UseCase 图,核心就是 actor,交互动作和商业价值,对应的 DSL 代码如下:
UseCase UC1_Example {
actor = "Insurance Employee"
interactions = create a "Customer", update a "Customer", "offer" a "Contract"
benefit = "I am able to manage the customers data and offer them insurance contracts."
}
在 Aggregate 聚合中,你可以设置 useCases 属性来描述对应的 UseCase,如下:
Aggregate Contract {
useCases = UC1_Example, UC2_Example
}
