Kea
Kea
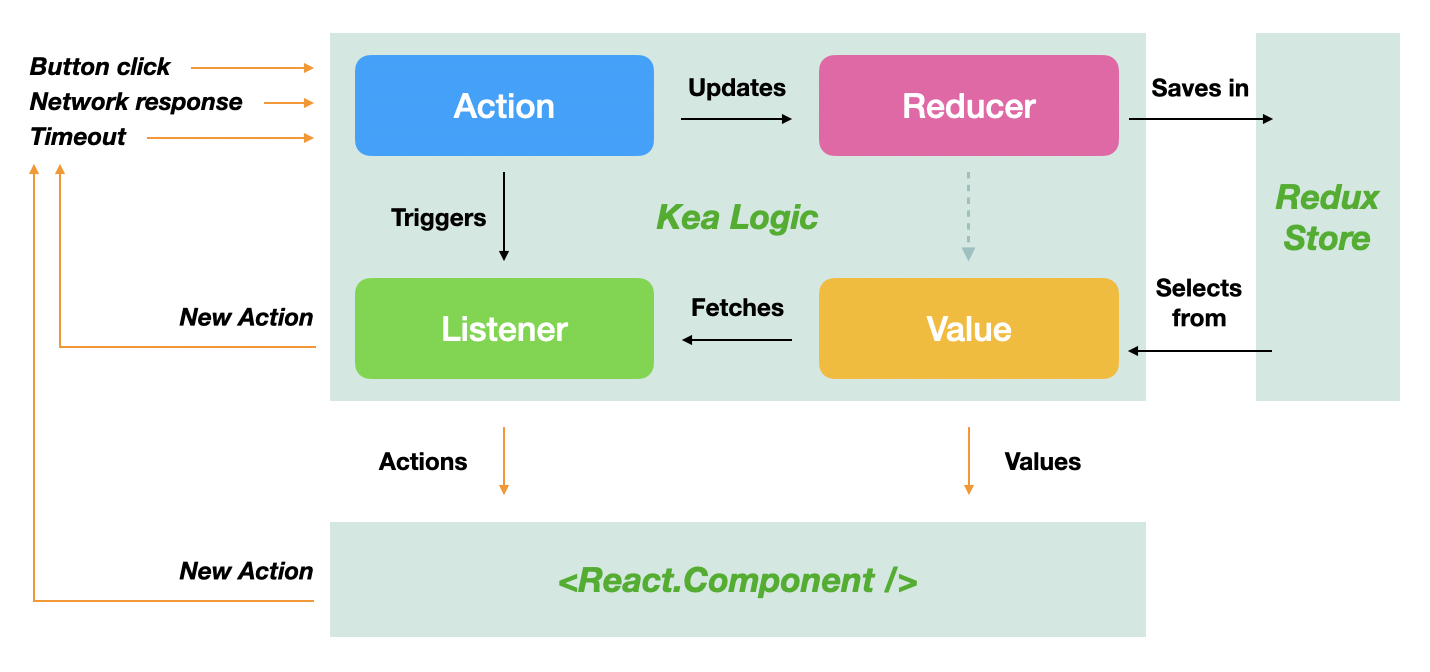
- 应用中的每个操作都以一个操作(递增计数器)开始。
- 这些操作将更新保存实际数据的减速器(计数器
) 。 - 此数据以全局状态存储,该状态由
Redux 管理。 - 您可以从此状态通过选择器(在状态中找到计数器)获取值(计数器为
1 ) 。 - 动作也可能触发侦听器,这些侦听器是与外部
API 对话,读取值或调度其他动作的纯异步函数。 - 所有相关的动作,缩减器,选择器和侦听器都分组为一个逻辑(counterLogic
) 。 React 组件连接到此逻辑并提取所有需要的动作和值。
核心概念
Actions
import { kea } from 'kea'
const logic = kea({ ... })
在
const logic = kea({
actions: () => ({
addToCounter: (amount) => ({ amount }),
setName: (name) => ({ name }),
submitForm: (values, page) => ({ values, page }),
actionWithoutArguments: true,
}),
});
将动作视为调度到队列的事件。他们自己什么也不做,减速器和侦听器(如下所述)等待操作并做出相应反应。
import { useActions } from "kea";
function BigButton() {
const { addToCounter } = useActions(logic);
return (
<button onClick={() => addToCounter(1000)}>Add one thousand! 🤩</button>
);
}
Reducer
const logic = kea({
actions: () => ({
increment: (amount) => ({ amount }),
decrement: (amount) => ({ amount }),
}),
reducers: () => ({
counter: [
0,
{
increment: (state, { amount }) => state + amount,
decrement: (state, { amount }) => state - amount,
},
],
}),
});
不过需要注意的是,
{
addTodo: (state, { todo }) => [...state, todo], // ❤️❤️❤️ Always do this!
addTodo: (state, { todo }) => state.push(todo), // ☠️☠️☠️ NEVER do this!
}
Listener
在
const logic = kea({
actions: () => ({
loadUsers: true,
setUsers: (users) => ({ users }),
}),
listeners: () => ({
loadUsers: async () => {
const users = await api.get("users");
actions.setUsers(users);
},
}),
reducers: () => ({
users: [
[],
{
setUsers: (_, { users }) => users,
},
],
}),
});
有时候我们在
const logic = kea({
// actions, reducers, ...
listeners: ({ actions, values }) => ({
fetchDetails: async () => {
const { username } = values; // 👈 get the latest username
const details = await api.fetchDetails({ username });
actions.setDetails(details);
},
}),
});
Selector
而
const logic = kea({
actions: () => ({
setMonth: (month) => ({ month }),
setRecords: (records) => ({ records }),
}),
reducers: () => ({
month: [
"2020-04",
{
setMonth: (_, { month }) => month,
},
],
records: [
[],
{
setRecords: (_, { records }) => records,
},
],
}),
selectors: ({ selectors }) => ({
recordsForSelectedMonth: [
() => [selectors.month, selectors.records],
(month, records) => {
return records.filter((r) => r.month === month);
},
],
}),
});
const { recordsForSelectedMonth } = useValues(logic);
在React 中使用
函数式组件
import { kea, useActions } from 'kea'
const logic = kea({ ... })
function MyComponent () {
const { increment } = useActions(logic)
return <button onClick={increment}>Increment</button>
}
import { kea, useValues } from 'kea'
const logic = kea({ ... })
function MyComponent () {
const { counter, doubleCounter } = useValues(logic)
return <div>{counter} * 2 = {doubleCounter}</div>
}
类组件
const logic = kea({
actions: () => ({
doSomething: true,
doSomethingElse: true,
}),
reducers: () => ({
firstOne: ["default", { doSomething: () => "did it" }],
secondOne: ["default", { doSomething: () => "did it" }],
}),
});
class MyComponent extends Component {
render() {
const { firstOne, secondOne } = this.props;
// The following two lines are equivalent as
// `this.actions` is a shorthand for `this.props.actions`
const { doSomething, doSomethingElse } = this.actions;
const { doSomething, doSomethingElse } = this.props.actions;
return <div />;
}
}
const MyConnectedComponent = logic(MyComponent);
import { connect } from "kea";
@connect({
actions: [menuLogic, ["openMenu", "closeMenu"]],
values: [menuLogic, ["isOpen as isMenuOpen"], accountLogic, ["currentUser"]],
})
class MyComponent extends Component {
render() {
const { currentUser } = this.props;
const { closeMenu } = this.actions;
return <button onClick={closeMenu}>{currentUser.name}</button>;
}
}
