类型判断与转换
JavaScript 中类型判断与转换
类型 / 格式判断与转换
typeof
typeof 运算符可以返回一个值的数据类型,可能有以下结果。
( 1)原始类型
数值、字符串、布尔值分别返回 number、string、boolean。
typeof 123; // "number"
typeof "123"; // "string"
typeof false; // "boolean"
( 2)函数
函数返回 function。
// 定义一个空函数
function f(){}
typeof f
// "function"
( 3)undefined
undefined 返回 undefined。
typeof undefined
// "undefined"
利用这一点,typeof 可以用来检查一个没有声明的变量,而不报错。
v
// ReferenceError: v is not defined
typeof v
// "undefined"
实际编程中,这个特点通常用在判断语句。
// 错误的写法
if (v){
// ...
}
// ReferenceError: v is not defined
// 正确的写法
if (typeof v === "undefined"){
// ...
}
( 4)其他
除此以外,都返回 object。
typeof window // "object"
typeof {} // "object"
typeof [] // "object"
typeof null // "object"
从上面代码可以看到,空数组([] )的类型也是 object,这表示在 JavaScript 内部,数组本质上只是一种特殊的对象。另外,null 的类型也是 object,这是由于历史原因造成的,为了兼容以前的代码,后来就没法修改了,并不是说 null 就属于对象,本质上 null 是一个类似于 undefined 的特殊值。
instanceof
typeof 对数组(array )和对象(object )的显示结果都是 object,那么怎么区分它们呢?instanceof 运算符可以做到。
const o = {};
const a = [];
o instanceof Array; // false
a instanceof Array; // true
类型的自动转换
当遇到以下几种情况,JavaScript 会自动转换数据类型:
- 不同类型的数据进行互相运算;
- 对非布尔值类型的数据求布尔值 ;
- 对非数值类型的数据使用一元运算符(即 “+” 和 “-”)。
动态类型检查
tcomb
npm install tcomb --save
A type-checked function:
import t from 'tcomb';
function sum(a, b) {
t.Number(a);
t.Number(b);
return a + b;
}
sum(1, 's'); // throws '[tcomb] Invalid value "s" supplied to Number'
A user defined type:
const Integer = t.refinement(t.Number, (n) => n % 1 === 0, 'Integer');
A type-checked class:
const Person = t.struct({
name: t.String, // required string
surname: t.maybe(t.String), // optional string
age: Integer, // required integer
tags: t.list(t.String) // a list of strings
}, 'Person');
// methods are defined as usual
Person.prototype.getFullName = function () {
return `${this.name} ${this.surname}`;
};
const person = Person({
surname: 'Canti'
}); // throws '[tcomb] Invalid value undefined supplied to Person/name: String'
类型判断
typeof
typeof 是 javascript 原生提供的判断数据类型的运算符,它会返回一个表示参数的数据类型的字符串,例如:
const s = 'hello';
console.log(typeof(s))//String
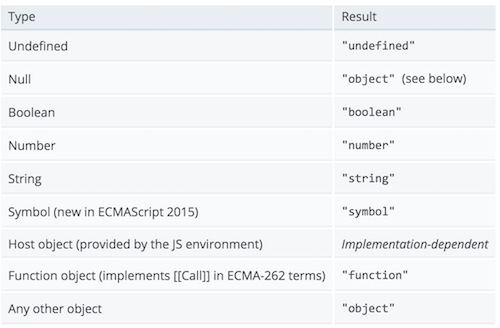
以下是我在 MDN 的文档中找到的一张包含 typeof 运算法的针对不同参数的输出结果的表格:
从这张表格可以看出,数组被归到了 Any other object 当中,所以 typeof 返回的结果应该是 Object,并没有办法区分数组,对象,null 等原型链上都有 Object 的数据类型。
const a = null;
const b = {};
const c= [];
console.log(typeof(a)); //Object
console.log(typeof(b)); //Object
console.log(typeof(c)); //Object
运行上面的代码就会发现,在参数为数组,对象或者 null 时,typeof 返回的结果都是 object,可以使用这种方法并不能识别出数组,因此,在 JavaScript 项目中用 typeof 来判断一个位置类型的数据是否为数组,是非常不靠谱的。
instanceof
既然 typeof 无法用于判断数组是否为数组,那么用 instance 运算符来判断是否可行呢?要回答这个问题,我们首先得了解 instanceof 运算法是干嘛用的。
instanceof 运算符可以用来判断某个构造函数的 prototype 属性所指向的對象是否存在于另外一个要检测对象的原型链上。在使用的时候语法如下:
object instanceof constructor
用我的理解来说,就是要判断一个 Object 是不是数组(这里不是口误,在 JavaScript 当中,数组实际上也是一种对象),如果这个 Object 的原型链上能够找到 Array 构造函数的话,那么这个 Object 应该及就是一个数组,如果这个 Object 的原型链上只能找到 Object 构造函数的话,那么它就不是一个数组。
const a = [];
const b = {};
console.log(a instanceof Array);//true
console.log(a instanceof Object);//true,在数组的原型链上也能找到Object构造函数
console.log(b instanceof Array);//false
由上面的几行代码可以看出,使用 instanceof 运算符可以分辨数组和对象,可以判断数组是数组。
constructor
实例化的数组拥有一个 constructor 属性,这个属性指向生成这个数组的方法。const a = []; console.log(a.constructor);//function Array(){ [native code] } 以上的代码说明,数组是有一个叫 Array 的函数实例化的。如果被判断的对象是其他的数据类型的话,结果如下: const o = {}; console.log(o.constructor);//function Object(){ [native code] } const r = /^[0-9]$/; console.log(r.constructor);//function RegExp() { [native code] } const n = null; console.log(n.constructor);// 报错看到这里,你可能会觉得这也是一种靠谱的判断数组的方法,我们可以用以下的方式来判断 : const a = []; console.log(a.constructor == Array);//true 但是,很遗憾的通知你,constructor 属性是可以改写的,如果你一不小心作死改了 constructor 属性的话,那么使用这种方法就无法 判断出数组的真是身份了,写到这里,我不禁想起了无间道的那段经典对白,梁朝伟:“ 对不起,我是警察。” 刘德华:“ 谁知道呢?”。// 定义一个数组 const a = []; // 作死将 constructor 属性改成了别的 a.contrtuctor = Object; console.log(a.constructor == Array);//false ( 哭脸 )console.log(a.constructor == Object);//true ( 哭脸 )console.log(a instanceof Array);//true (instanceof 火眼金睛 ) 可以看出,constructor 属性被修改之后,就无法用这个方法判断数组是数组了,除非你能保证不会发生 constructor 属性被改写的情况,否则用这种方法来判断数组也是不靠谱的。
toString
另一个行之有效的方法就是使用 Object.prototype.toString 方法来判断,每一个继承自 Object 的对象都拥有 toString 的方法。
如果一个对象的 toString 方法没有被重写过的话,那么 toString 方法将会返回 “[object type]",其中的type代表的是对象的类型,根据 type 的值,我们就可以判断这个疑似数组的对象到底是不是数组了。
你可能会纠结,为什么不是直接调用数组,或则字符串自己的的 toString 方法呢?我们试一试就知道了。
const a = ['Hello','Howard'];
const b = {0:'Hello',1:'Howard'};
const c = 'Hello Howard';
a.toString();//"Hello,Howard"
b.toString();//"[object Object]"
c.toString();//"Hello,Howard"
从上面的代码可以看出,除了对象之外,其他的数据类型的 toString 返回的都是内容的字符创,只有对象的 toString 方法会返回对象的类型。所以要判断除了对象之外的数据的数据类型,我们需要 “ 借用 ” 对象的 toString 方法,所以我们需要使用 call 或者 apply 方法来改变 toString 方法的执行上下文。
const a = ['Hello','Howard'];
const b = {0:'Hello',1:'Howard'};
const c = 'Hello Howard';
Object.prototype.toString.call(a);//"[object Array]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(b);//"[object Object]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(c);//"[object String]"
使用 apply 方法也能达到同样的效果:
const a = ["Hello", "Howard"];
const b = { 0: "Hello", 1: "Howard" };
const c = "Hello Howard";
Object.prototype.toString.apply(a); //"[object Array]"
Object.prototype.toString.apply(b); //"[object Object]"
Object.prototype.toString.apply(c); //"[object String]"
总结一下,我们就可以用写一个方法来判断数组是否为数组:
const isArray = (something)=>{
return Object.prototype.toString.call(something) === '[object Array]';
}
cosnt a = [];
const b = {};
isArray(a);//true
isArray(b);//false
但是,如果你非要在创建这个方法之前这么来一下,改变了 Object 原型链上的 toString 方法,那我真心帮不了你了 …
//重写了toString方法
Object.prototype.toString = () => {
alert("你吃过了么?");
};
//调用String方法
const a = [];
Object.prototype.toString.call(a); //弹框问你吃过饭没有
当然了,只有在浏览器当中才能看到 alert 弹框,这个我就不解释了。
属性判断
obj.prop !== undefined: compare against undefined directly typeof obj.prop !== ‘undefined’: verify the property value type obj.hasOwnProperty(‘prop’): verify whether the object has an own property ‘prop’ in obj: verify whether the object has an own or inherited property
隐式类型转换
在 JavaScript 中,当我们进行比较操作或者加减乘除四则运算操作时,常常会触发 JavaScript 的隐式类型转换机制;而这部分也往往是令人迷惑的地方。譬如浏览器中的 console.log 操作常常会将任何值都转化为字符串然后展示,而数学运算则会首先将值转化为数值类型(除了 Date 类型对象)然后进行操作。
我们首先来看几组典型的 JavaScript 中运算符操作结果,希望阅读完本部分之后能够对每一个条目都能进行合理解释:
// 比较
[] == ![] // true
NaN !== NaN // true
1 == true // true
2 == true // false
"2" == true // flase
null > 0 // false
null < 0 // false
null == 0 // false
null >= 0 // true
// 加法
true + 1 // 1
undefined + 1 // NaN
let obj = {};
{} + 1 // 1,这里的 {} 被当成了代码块
{ 1 + 1 } + 1 // 1
obj + 1 // [object Object]1
{} + {} // Chrome 上显示 "[object Object][object Object]",Firefox 显示 NaN
[] + {} // [object Object]
[] + a // [object Object]
+ [] // 等价于 + "" => 0
{} + [] // 0
a + [] // [object Object]
[2,3] + [1,2] // '2,31,2'
[2] + 1 // '21'
[2] + (-1) // "2-1"
// 减法或其他操作,无法进行字符串连接,因此在错误的字符串格式下返回 NaN
[2] - 1 // 1
[2,3] - 1 // NaN
{} - 1 // -1
原始类型间转换
JavaScript 中我们常说的原始类型包括了数值类型、字符串类型、布尔类型与空类型这几种;而我们常用的原始类型之间的转换函数就是 String、Number 与 Boolean:
// String
let value = true;
console.log(typeof value); // boolean
value = String(value); // now value is a string "true"
console.log(typeof value); // string
// Number
let str = "123";
console.log(typeof str); // string
let num = Number(str); // becomes a number 123
console.log(typeof num); // number
let age = Number("an arbitrary string instead of a number");
console.log(age); // NaN, conversion failed
// Boolean
console.log(Boolean(1)); // true
console.log(Boolean(0)); // false
console.log(Boolean("hello")); // true
console.log(Boolean("")); // false
最终,我们可以得到如下的 JavaScript 原始类型转换表(包括复合类型向原始类型转换的范例):
| 原始值 | 转化为数值类型 | 转化为字符串类型 | 转化为 Boolean 类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| false | 0 | “false” | false |
| true | 1 | “true” | true |
| 0 | 0 | “0” | false |
| 1 | 1 | “1” | true |
| “0” | 0 | “0” | true |
| “1” | 1 | “1” | true |
| NaN | NaN | “NaN” | false |
| Infinity | Infinity | “Infinity” | true |
| -Infinity | -Infinity | “-Infinity” | true |
| "” | 0 | "" | false |
| “20” | 20 | “20” | true |
| “twenty” | NaN | “twenty” | true |
| [ ] | 0 | "" | true |
| [20] | 20 | “20” | true |
| [10,20] | NaN | “10,20” | true |
| [“twenty”] | NaN | “twenty” | true |
| [“ten”,“twenty”] | NaN | “ten,twenty” | true |
| function(){} | NaN | “function(){}” | true |
| { } | NaN | “[object Object]” | true |
| null | 0 | “null” | false |
| undefined | NaN | “undefined” | false |
更多比较表格参考 JavaScript-Equality-Table。
ToPrimitive
在比较运算与加法运算中,都会涉及到将运算符两侧的操作对象转化为原始对象的步骤;而 JavaScript 中这种转化实际上都是由 ToPrimitive 函数执行的。实际上,当某个对象出现在了需要原始类型才能进行操作的上下文时,JavaScript 会自动调用 ToPrimitive 函数将对象转化为原始类型;譬如上文介绍的 alert 函数、数学运算符、作为对象的键都是典型场景,该函数的签名如下:
ToPrimitive(input, PreferredType?)
为了更好地理解其工作原理,我们可以用 JavaScript 进行简单地实现:
const ToPrimitive = function (obj, preferredType) {
const APIs = {
typeOf: function (obj) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj).slice(8, -1);
},
isPrimitive: function (obj) {
const _this = this,
types = ["Null", "Undefined", "String", "Boolean", "Number"];
return types.indexOf(_this.typeOf(obj)) !== -1;
},
}; // 如果 obj 本身已经是原始对象,则直接返回
if (APIs.isPrimitive(obj)) {
return obj;
} // 对于 Date 类型,会优先使用其 toString 方法;否则优先使用 valueOf 方法
preferredType =
preferredType === "String" || APIs.typeOf(obj) === "Date"
? "String"
: "Number";
if (preferredType === "Number") {
if (APIs.isPrimitive(obj.valueOf())) {
return obj.valueOf();
}
if (APIs.isPrimitive(obj.toString())) {
return obj.toString();
}
} else {
if (APIs.isPrimitive(obj.toString())) {
return obj.toString();
}
if (APIs.isPrimitive(obj.valueOf())) {
return obj.valueOf();
}
}
throw new TypeError("TypeError");
};
我们可以简单覆写某个对象的 valueOf 方法,即可以发现其运算结果发生了变化:
let obj = {
valueOf: () => {
return 0;
},
};
obj + 1; // 1
如果我们强制将某个对象的 valueOf 与 toString 方法都覆写为返回值为对象的方法,则会直接抛出异常。
obj = {
valueOf: function () {
console.log("valueOf");
return {}; // not a primitive
},
toString: function () {
console.log("toString");
return {}; // not a primitive
}
}
obj + 1
// error
Uncaught TypeError: Cannot convert object to primitive value
at <anonymous>:1:5
值得一提的是对于数值类型的 valueOf() 函数的调用结果仍为数组,因此数组类型的隐式类型转换结果是字符串。而在 ES6 中引入 Symbol 类型之后,JavaScript 会优先调用对象的 [Symbol.toPrimitive] 方法来将该对象转化为原始类型,那么方法的调用顺序就变为了:
- 当
obj[Symbol.toPrimitive](preferredType)方法存在时,优先调用该方法; - 如果 preferredType 参数为 String,则依次尝试
obj.toString()与obj.valueOf(); - 如果 preferredType 参数为 Number 或者默认值,则依次尝试
obj.valueOf()与obj.toString()。
而 [Symbol.toPrimitive] 方法的签名为:
obj[Symbol.toPrimitive] = function(hint) {
// return a primitive value
// hint = one of "string", "number", "default"
}
我们同样可以通过覆写该方法来修改对象的运算表现:
user = {
name: "John",
money: 1000,
[Symbol.toPrimitive](hint) {
console.log(`hint: ${hint}`);
return hint == "string" ? `{name: "${this.name}"}` : this.money;
},
};
// conversions demo:
console.log(user); // hint: string -> {name: "John"}
console.log(+user); // hint: number -> 1000
console.log(user + 500); // hint: default -> 1500
比较运算
JavaScript 为我们提供了严格比较与类型转换比较两种模式,严格比较(=== )只会在操作符两侧的操作对象类型一致,并且内容一致时才会返回为 true,否则返回 false。而更为广泛使用的 == 操作符则会首先将操作对象转化为相同类型,再进行比较。对于 <= 等运算,则会首先转化为原始对象(Primitives ),然后再进行对比。
标准的相等性操作符(== 与 !=)使用了Abstract Equality Comparison Algorithm来比较操作符两侧的操作对象(x == y ),该算法流程要点提取如下:
- 如果 x 或 y 中有一个为 NaN,则返回 false;
- 如果 x 与 y 皆为 null 或 undefined 中的一种类型,则返回 true(null == undefined // true );否则返回 false(null == 0 // false );
- 如果 x,y 类型不一致,且 x,y 为 String、Number、Boolean 中的某一类型,则将 x,y 使用 toNumber 函数转化为 Number 类型再进行比较;
- 如果 x,y 中有一个为 Object,则首先使用 ToPrimitive 函数将其转化为原始类型,再进行比较。
- 如果 x,y 皆为 Object,则进行 Reference 比较;譬如 [] ==
我们再来回顾下文首提出的 [] == ![] 这个比较运算,首先 [] 为对象,则调用 ToPrimitive 函数将其转化为字符串 "";对于右侧的 ![],首先会进行显式类型转换,将其转化为 false。然后在比较运算中,会将运算符两侧的运算对象都转化为数值类型,即都转化为了 0,因此最终的比较结果为 true。在上文中还介绍了 null >= 0 为 true 的这种比较结果,在 ECMAScript 中还规定,如果 < 为 false,则 >= 为 true。
加法运算
对于加法运算而言,JavaScript 首先会将操作符两侧的对象转换为 Primitive 类型;然后当适当的隐式类型转换能得出有意义的值的前提下,JavaScript 会先进行隐式类型转换,再进行运算。譬如 value1 + value2 这个表达式,首先会调用 ToPrimitive 函数将两个操作数转化为原始类型:
prim1 := ToPrimitive(value1)
prim2 := ToPrimitive(value2)
这里将会优先调用除了 Date 类型之外对象的 valueOf 方法,而因为数组的 valueOf 方法的返回值仍为数组类型,则会返回其字符串表示。而经过转换之后的 prim1 与 prim2 中的任一个为字符串,则会优先进行字符串连接;否则进行加法计算。