表操作
Create:表创建
Create Table 用于在 Hive 中创建表,其语法如下所示,注意,Hive 中的表名列名不区分大小写:
CREATE [TEMPORARY] [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.] table_name
[(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[COMMENT table_comment]
[ROW FORMAT row_format]
[STORED AS file_format]
譬如当我们希望创建如下的包含 Employee 新的表时,数据格式和域如下:
| Sr.No | Field Name | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Eid | int |
| 2 | Name | String |
| 3 | Salary | Float |
| 4 | Designation | string |
| 然后如下的语句会指定该表的注释、不同的域的分隔符、不同的行的分隔符,以及存储的文件类型: |
COMMENT ‘Employee details’
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘\t’
LINES TERMINATED BY ‘\n’
STORED IN TEXT FILE
然后完整的创建语句为:
hive> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS employee ( eid int, name String,
salary String, destination String)
COMMENT ‘Employee details’
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘\t’
LINES TERMINATED BY ‘\n’
STORED AS TEXTFILE;
如果你添加了IF NOT EXISTS选项,Hive 会在表存在的情况下忽略掉创建,在成功执行该语句之后,你会得到如下的响应:
OK
Time taken: 5.905 seconds
hive>
Java Programming
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
public class HiveCreateTable {
private static String driverName = "org.apache.hadoop.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver";
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
// Register driver and create driver instance
Class.forName(driverName);
// get connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:hive://localhost:10000/userdb", "", "");
// create statement
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
// execute statement
stmt.executeQuery("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "
+" employee ( eid int, name String, "
+" salary String, destignation String)"
+" COMMENT ‘Employee details’"
+" ROW FORMAT DELIMITED"
+" FIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘\t’"
+" LINES TERMINATED BY ‘\n’"
+" STORED AS TEXTFILE;");
System.out.println(“ Table employee created.”);
con.close();
}
}
内表 VS 外表
Hive 默认创建的表为内部表,内部表与外部表的区别可以归纳为:
- 在导入数据到外部表,数据并没有移动到自己的数据仓库目录下(如果指定了 location 的话),也就是说外部表中的数据并不是由它自己来管理的!而内部表则不一样;
- 在删除内部表的时候,Hive 将会把属于表的元数据和数据全部删掉;而删除外部表的时候,Hive 仅仅删除外部表的元数据,数据是不会删除的!
- 在创建内部表或外部表时加上 location 的效果是一样的,只不过表目录的位置不同而已,加上 partition 用法也一样,只不过表目录下会有分区目录而已,load data local inpath 直接把本地文件系统的数据上传到 hdfs 上,有 location 上传到 location 指定的位置上,没有的话上传到 hive 默认配置的数据仓库中。
内表
(1)创建不带分区的内表 首先创建一个表,注意,Hive 创建成功的表即使你输入的是大写,也会被转化为小写:
create table innertable(id int,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by '|';
然后我们从 HDFS 上加载数据:
load data inpath 'hdfs://master:9000/user/root/test/innerTable' into table innertable;
查看 HDFS 上/user/root/test/innerTable,发现文件价 innerTable 还在,但是里面的文件已经不在了。去哪了,去 innertable 表中了。然后删除刚刚创建的表:
drop table innertable;
到 HDFS 上看一下 innertable 文件夹及其中的文件都没有了。去哪了,删除表的时候删除了。 (2)带分区的内表 使用如下命令创建表:
create table inner_table_with_p(id int,name string) partitioned by (part_num int);
#从HDFS加载数据
load data inpath 'hdfs://master:9000/user/root/test/innerTable/part1' into table inner_table_with_p partition(part_num=1)(文件夹inner_table_with_p出现子文件夹part_num=1,innerTable中 part1消失);
load data inpath 'hdfs://master:9000/user/root/test/innerTable/part2' into table inner_table_with_p partition(part_num=2)(文件夹inner_table_with_p出现子文件夹part_num=2,innerTable中 part2消失);
load data inpath ‘hdfs://master:9000/user/root/test/innerTable/part3’ into table inner_table_with_p partition(part_num=3)(文件夹 inner_table_with_p 出现子文件夹 part_num=3,innerTable 中 part3 消失);#删除分区
alter table inner_table_with_p drop partition(part_num=1);(part_num=1 对应分区文件夹本删除)
#删除表
drop table inner_table_with_p;(HDFS 上 inner_table_with_p 文件夹被删除)
外表
(1)不带分区的外表
创建表
create external table outer_table(id int,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘|’; (hive 仓储目录中出现 outer_table)
加载数据
load data inpath ‘/user/root/test/outerTable/outer’ into table outer_table;(outer_table 中出现子文件 outer,outerTable 中 outer 消失)
删除表
drop table outer_table; (outer_table 及子文件 outer 依然存在,因为这是外表)
(2)带分区的外表
创建表
create external table outer_table_with_p(id int,name string) partitioned by (part_num int) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘|’; (hive 仓储目录中出现 outer_table_with_p)
加载数据
load data inpath ‘/user/root/test/outerTable/part1’ into table outer_table_with_p partiton(part_num=1); (outer_table_with_p 中出现子文件夹 part_num=1)
load data inpath ‘/user/root/test/outerTable/part2’ into table outer_table_with_p partition(part_num=2);(outer_table_with_p 中出现子文件夹 part_num=2)
load data inpath ‘/user/root/test/outerTable/part3’ into table outer_table_with_p partition(part_num=3);(outer_table_with_p 中出现子文件夹 part_num=3)
删除分区
alter table outer_table_with_p drop partition(part_num=1);(HDFS 上分区文件依旧存在)
删除表
drop table outer_table_with_p;(HDFS 上对应数据依旧存在)
Partition:表分区
在 Hive Select 查询中一般会扫描整个表内容,会消耗很多时间做没必要的工作。有时候只需要扫描表中关心的一部分数据,因此建表时引入了 partition 概念。分区表指的是在创建表时指定的 partition 的分区空间。Hive 可以对数据按照某列或者某些列进行分区管理,所谓分区我们可以拿下面的例子进行解释。当前互联网应用每天都要存储大量的日志文件,几 G、几十 G 甚至更大都是有可能。存储日志,其中必然有个属性是日志产生的日期。在产生分区时,就可以按照日志产生的日期列进行划分。把每一天的日志当作一个分区。将数据组织成分区,主要可以提高数据的查询速度。至于用户存储的每一条记录到底放到哪个分区,由用户决定。即用户在加载数据的时候必须显示的指定该部分数据放到哪个分区。创建表分区的语法格式为:
CREATE [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name
[(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[COMMENT table_comment]
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...) [SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS]
[ROW FORMAT row_format]
[STORED AS file_format]
[LOCATION hdfs_path]
分区创建
单分区
- 创建一个分区表,以 ds 为分区列:
create table invites (id int, name string) partitioned by (ds string) row format delimited fields terminated by 't' stored as textfile;
- 将数据添加到时间为 2013-08-16 这个分区中:
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/Desktop/data.txt' overwrite into table invites partition (ds='2013-08-16');
- 将数据添加到时间为 2013-08-20 这个分区中:
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/Desktop/data.txt' overwrite into table invites partition (ds='2013-08-20');
- 从一个分区中查询数据:
select * from invites where ds ='2013-08-12';
- 往一个分区表的某一个分区中添加数据:
insert overwrite table invites partition (ds='2013-08-12') select id,max(name) from test group by id;
可以查看分区的具体情况,使用命令:
hadoop fs -ls /home/hive/warehouse/invites
或者:
show partitions tablename;
Bucket:桶
对于每一个表(table)或者分区,Hive 可以进一步组织成桶,也就是说桶是更为细粒度的数据范围划分。Hive 也是针对某一列进行桶的组织。Hive 采用对列值哈希,然后除以桶的个数求余的方式决定该条记录存放在哪个桶当中。把表(或者分区)组织成桶(Bucket)有两个理由:
- 获得更高的查询处理效率。桶为表加上了额外的结 构,Hive 在处理有些查询时能利用这个结构。具体而言,连接两个在(包含连接列的)相同列上划分了桶的表,可以使用 Map 端连接 (Map-side join)高效的实现。比如 JOIN 操作。对于 JOIN 操作两个表有一个相同的列,如果对这两个表都进行了桶操作。那么将保存相同列值的桶进行 JOIN 操 作就可以,可以大大较少 JOIN 的数据量。
- 使取样(sampling)更高效。在处理大规模数据集时,在开发和修改查询的阶段,如果能在数据集的一小部分数据上试运行查询,会带来很多方便。
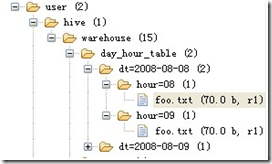
多分区
双分区建表语句:create table day_hour_table (id int, content string) partitioned by (dt string, hour string);双分区表,按天和小时分区,在表结构中新增加了 dt 和 hour 两列。