主从多线程模型
主从多线程模型
服务端用于接收客户端连接的不是 1 个单独的 NIO 线程了,而是采用独立的 NIO 线程池。Acceptor 接收 TCP 连接请求处理完成之后,将创建新的 SocketChannel 注册到处理连接的 IO 线程池中的某个 IO 线程上,有它去处理 IO 读写以及编解码的工作。Acceptor 只用于客户端登录、握手以及认证,一旦连接成功之后,将链路注册到线程池的 IO 线程上。

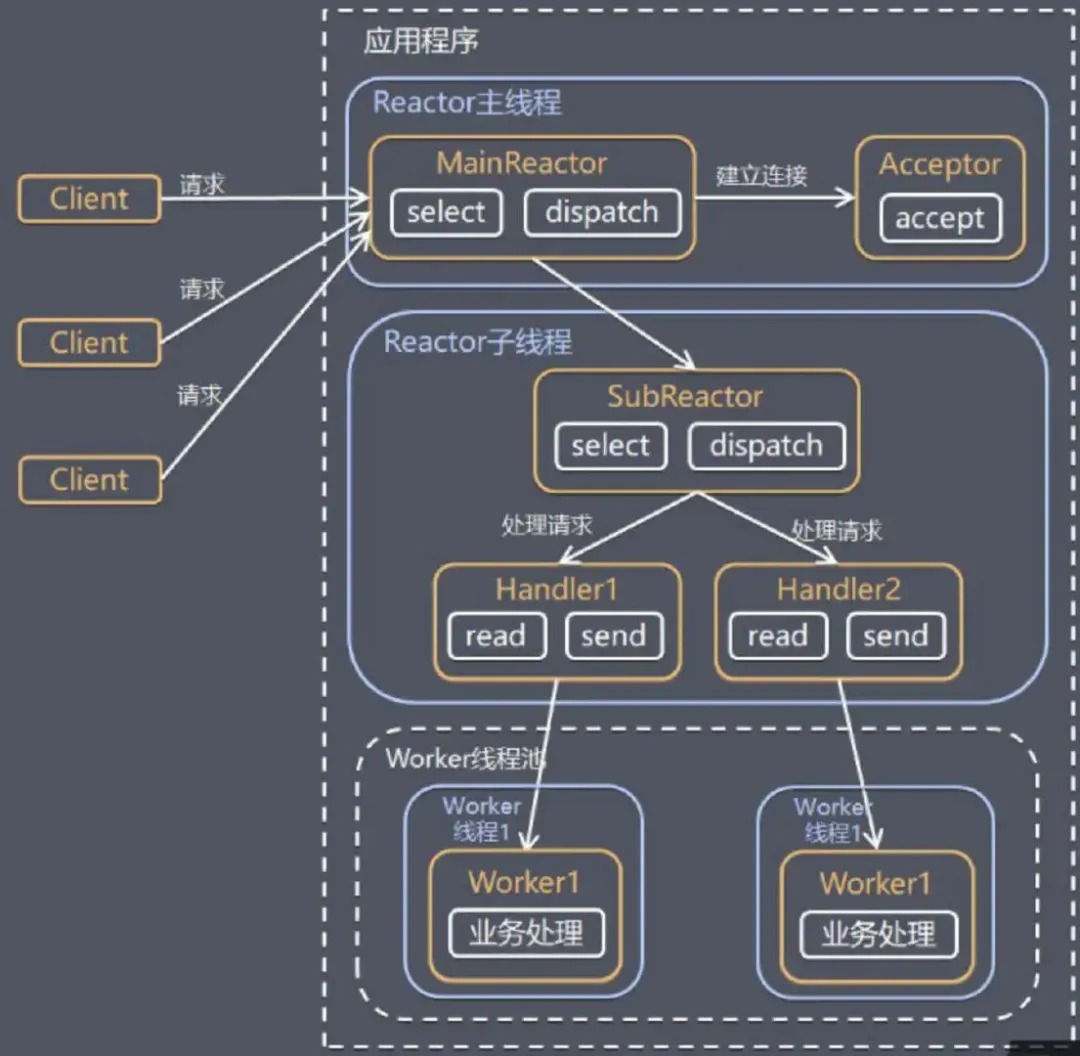
这种模型是将 Reactor 分成两部分,mainReactor 负责监听 server socket、accept 新连接,并将建立的 socket 分派给 subReactor;subReactor 负责多路分离已连接的 socket,读写网络数据;而对业务处理的功能,交给 worker 线程池来完成。
代码案例
public class Reactor implements Runnable {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
Selector selector;
public Reactor(int port) {
try {
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
selectionKey.attach(new Acceptor(serverSocketChannel));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
dispatcher(selectionKey);
iterator.remove();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void dispatcher(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
Runnable runnable = (Runnable) selectionKey.attachment();
runnable.run();
}
}
public class Acceptor implements Runnable {
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private final int core = 8;
private int index;
private SubReactor[] subReactors = new SubReactor[core];
private Thread[] threads = new Thread[core];
private final Selector[] selectors = new Selector[core];
public Acceptor(ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel) {
this.serverSocketChannel = serverSocketChannel;
for (int i = 0; i < core; i++) {
try {
selectors[i] = Selector.open();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
subReactors[i] = new SubReactor(selectors[i]);
threads[i] = new Thread(subReactors[i]);
threads[i].start();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("acceptor thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("有客户端连接上来了," + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
selectors[index].wakeup();
SelectionKey selectionKey = socketChannel.register(selectors[index], SelectionKey.OP_READ);
selectionKey.attach(new WorkerHandler(socketChannel));
if (++index == threads.length) {
index = 0;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class SubReactor implements Runnable {
private Selector selector;
public SubReactor(Selector selector) {
this.selector = selector;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
selector.select();
System.out.println("selector:" + selector.toString() + "thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
dispacher(selectionKey);
iterator.remove();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void dispacher(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
Runnable runnable = (Runnable) selectionKey.attachment();
runnable.run();
}
}
public class WorkerHandler implements Runnable {
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
public WorkerHandler(SocketChannel socketChannel) {
this.socketChannel = socketChannel;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("workHandler thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
socketChannel.read(buffer);
String message = new String(buffer.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + "发来的消息:" + message);
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("你的消息我收到了".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
acceptor thread:main
有客户端连接上来了,/127.0.0.1:65194
selector:sun.nio.ch.KQueueSelectorImpl@5a506132thread:Thread-0
selector:sun.nio.ch.KQueueSelectorImpl@5a506132thread:Thread-0
workHandler thread:Thread-0
/127.0.0.1:65194发来的消息:123
acceptor thread:main
有客户端连接上来了,/127.0.0.1:65202
selector:sun.nio.ch.KQueueSelectorImpl@59887d72thread:Thread-1
selector:sun.nio.ch.KQueueSelectorImpl@59887d72thread:Thread-1
workHandler thread:Thread-1
/127.0.0.1:65202发来的消息:444
**/
可以很清楚的看到,从始至终,acceptor 都只有一个 main 线程,而负责处理客户端写请求的是不同的线程,而且还是不同的 reactor、selector。
