SQL-CheatSheet
SQL 语法速览与备忘清单
SQL 是 Structrued Query Language 的缩写,即结构化查询语言。它是负责与 ANSI(美国国家标准学会)维护的数据库交互的标准。作为关系数据库的标准语言,它已被众多商用 DBMS 产品所采用,使得它已成为关系数据库领域中一个主流语言,不仅包含数据查询功能,还包括插入、删除、更新和数据定义功能。最为重要的 SQL92 版本的详细标准可以查看这里,或者在 Wiki 上查看 SQL 标准的变化。
- DDL 是数据定义语言的简称,它涉及到数据库模式和描述,即数据应该如何在数据库中存在。
- DML 是数据操作语言的简称,它处理数据操作,包括最常见的 SQL 语句,如 SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE 等,它被用来存储、修改、检索、删除和更新数据库中的数据。
- DCL 是数据控制语言的简称,包括 GRANT 等命令,主要涉及数据库系统的权利、权限和其他控制。
数据类型
Text types
| 数据类型 | 说明 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CHAR(size) | 保存一个固定长度的字符串(可以包含字母、数字和特殊字符)。固定的大小在括号中指定。最多可以存储 255 个字符。 | ||
| VARCHAR(size) | 存放一个可变长度的字符串(可以包含字母、数字和特殊字符)。最大的尺寸在括号中指定。最多可以存储 255 个字符。注意:如果你输入一个大于 255 的值,它将被转换成 TEXT 类型。 | ||
| TINYTEXT | 保存一个最大长度为 255 个字符的字符串。 | ||
| TEXT | 保存一个最大长度为 65,535 个字符的字符串。 | ||
| BLOB | 用于 BLOB(二进制大型对象)。最多可以容纳 65,535 个字节的数据 | BLOB | |
| MEDIUMTEXT | 存储一个最大长度为 16,777,215 个字符的字符串 | ||
| MEDIUMBLOB | 用于 BLOB(二进制大型对象)。最多可以容纳 16,777,215 字节的数据。 | ||
| LONGTEXT | 保存最大长度为 4,294,967,295 个字符的字符串 | ||
| LONGBLOB | 用于 BLOB(二进制大型对象)。最多可以容纳 4,294,967,295 字节的数据。 | ||
| ENUM(x,y,z,etc.) | 让你输入一个可能的值列表。在一个 ENUM 列表中,你最多可以列出 65535 个值。如果插入一个不在列表中的值,将插入一个空白值。注意:值是按照你输入的顺序排序的。你以这种格式输入可能的值。ENUM(‘X’,‘Y’,‘Z’) | ||
| SET | 与 ENUM 类似,只是 SET 最多可以包含 64 个列表项,并且可以存储多个选择 |
Number types
| 数据类型 | 说明 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TINYINT(size) | -128 to 127 normal. 0 到 255 UNSIGNED*。可以在括号内指定最大的数字数 |
SMALLINT(size) | |
| SMALLINT(size) | -32768 至 32767 正常。0 至 65535 UNSIGNED*。可以在括号中指定最大的数字数。 |
||
| MEDIUMINT(size) | -8388608 至 8388607 正常。0 至 16777215 UNSIGNED*。可以在括号内指定最大的数字数 |
INT(size) | |
| INT(size) | -2147483648 至 2147483647 正常。0 至 4294967295 UNSIGNED*。可以在括号内指定最大的数字数 |
BIGINT(size) | |
| BIGINT(size) | -9223372036854775808 至 9223372036854775807 正常。0 到 18446744073709551615 UNSIGNED*。可以在括号中指定最大的数字数 |
||
| FLOAT(size,d) | 一个带有浮动小数点的小数字。最大的数字数可以在 size 参数中指定。小数点右边的最大位数可在 d 参数中指定。 | ||
| DOUBLE(size,d) | 一个带有浮动小数点的大数字。可在 size 参数中指定最大位数。小数点右边的最大位数在 d 参数中指定。 | ||
| DECIMAL(size,d) | 一个以字符串形式存储的 DOUBLE,允许使用固定的小数点。最大的数字数可以在 size 参数中指定。小数点右边的最大位数在 d 参数中指定。 |
Date types
| 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| DATE() | 一个日期。格式。格式:YYYY-MM-DDN 注:支持的范围是'1000-01-01’到'9999-12-31’。 |
| DATETIME() | 一个日期和时间的组合。格式。YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SSNote: 支持的范围是从'1000-01-01 00:00:00’到'9999-12-31 23:59:59’。 |
| TIMESTAMP() | 一个时间戳。TIMESTAMP 值是以 Unix 纪元(‘1970-01-01 00:00:00’UTC)以来的秒数存储。格式。YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SSNote: 支持的范围是从'1970-01-01 00:00:01’ UTC 到'2038-01-09 03:14:07’ UTC。 |
| 时间()|一个时间。格式。HH:MI:SS 注:支持的范围是从’-838:59:59’到'838:59:59’。 | 年份() | 两位数或四位数格式的年份。注:允许四位数格式的数值。1901 至 2155。允许的两位数格式的值。70 至 69,代表 1970 年至 2069 年的年份。
基础语法
库
-- Comments start with two hyphens. End each command with a semicolon.
-- SQL is not case-sensitive about keywords. The sample commands here
-- follow the convention of spelling them in upper-case because it makes
-- it easier to distinguish them from database, table, and column names.
-- Create and delete a database. Database and table names are case-sensitive.
CREATE DATABASE someDatabase;
DROP DATABASE someDatabase;
-- List available databases.
SHOW DATABASES;
-- Use a particular existing database.
USE employees;
表
-- Create a table called tablename1, with the two columns shown, for
-- the database currently in use. Lots of other options are available
-- for how you specify the columns, such as their datatypes.
/**
CREATE TABLE <table_name1> (
<col_name1> <col_type1>,
<col_name2> <col_type2>,
<col_name3> <col_type3>
PRIMARY KEY (<col_name1>),
FOREIGN KEY (<col_name2>) REFERENCES <table_name2>(<col_name2>)
);
**/
CREATE TABLE tablename1 (fname VARCHAR(20), lname VARCHAR(20));
-- Check if not exit and create
create database if not exists `test`;
USE `test`;
SET @OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@@FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS, FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tblsample` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL auto_increment,
`recid` int(11) NOT NULL default '0',
`cvfilename` varchar(250) NOT NULL default '',
`cvpagenumber` int(11) NULL,
`cilineno` int(11) NULL,
`batchname` varchar(100) NOT NULL default '',
`type` varchar(20) NOT NULL default '',
`data` varchar(100) NOT NULL default '',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
IF OBJECT_ID('tbl_kunde', N'U') is not null
drop table tbl_kunde;
GO
create table tbl_kunde (
id_kunde int not null primary key,
fi_moral_nr int,
name varchar(25) not null,
vorname varchar not null,
wohnort varchar
);
GO
-- Insert a row of data into the table tablename1. This assumes that the
-- table has been defined to accept these values as appropriate for it.
INSERT INTO tablename1 VALUES('Richard','Mutt');
-- In tablename1, change the fname value to 'John'
-- for all rows that have an lname value of 'Mutt'.
UPDATE tablename1 SET fname='John' WHERE lname='Mutt';
-- Delete rows from the tablename1 table
-- where the lname value begins with 'M'.
DELETE FROM tablename1 WHERE lname like 'M%';
-- Delete all rows from the tablename1 table, leaving the empty table.
DELETE FROM tablename1;
-- Remove the entire tablename1 table.
DROP TABLE tablename1;
-- Foreign Key
ALTER TABLE tbl_kunde ADD CONSTRAINT FK_fi_moral_nr FOREIGN KEY (fi_moral_nr)
REFERENCES tkey_moral
ON UPDATE CASCADE
ON DELETE SET NULL;
-- Constraint
ALTER TABLE tkey_moral ADD CONSTRAINT PK_id_moral_nr PRIMARY KEY (id_moral_nr);
ALTER TABLE tbl_kunde ADD CONSTRAINT FK_fi_moral_nr FOREIGN KEY (fi_moral_nr)
REFERENCES tkey_moral
ON UPDATE CASCADE
ON DELETE SET NULL;
索引
-- Create
create unique index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde (name)
-- Disable
alter index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde disable
-- Rebuild
alter index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde rebuild
-- Reorganize
alter index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde reorganize
-- Drop
drop index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde
-- Alter
drop index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde
查询
| Name | Command |
|---|---|
| Select with regexp in where clause | select * from expenses where date regexp '2013-0[4-5]' limit 2; |
| Select with like in where clause | select * from expenses where date like '2013-0%' limit 2; |
| Select unix timestamp | select unix_timestamp(createtime) from expenses limit 1; |
| Offset limit | select * from student limit 4 offset 9 |
| Use replace function | UPDATE tb1 SET f1=REPLACE(f1, 'abc', 'def'); |
| Use if function | select Db, IF(IFNULL(User, “”)=”“, DB, User) from db; |
-- Select all rows and columns from the current database's departments table.
-- Default activity is for the interpreter to scroll the results on your screen.
SELECT * FROM departments;
-- Retrieve all rows from the departments table,
-- but only the dept_no and dept_name columns.
-- Splitting up commands across lines is OK.
SELECT dept_no,
dept_name FROM departments;
-- Retrieve all departments columns, but just 5 rows.
SELECT * FROM departments LIMIT 5;
-- Retrieve dept_name column values from the departments
-- table where the dept_name value has the substring 'en'.
SELECT dept_name FROM departments WHERE dept_name LIKE '%en%';
-- Retrieve all columns from the departments table where the dept_name
-- column starts with an 'S' and has exactly 4 characters after it.
SELECT * FROM departments WHERE dept_name LIKE 'S____';
-- Select title values from the titles table but don't show duplicates.
SELECT DISTINCT title FROM titles;
-- Same as above, but sorted (case-sensitive) by the title values.
SELECT DISTINCT title FROM titles ORDER BY title;
-- Show the number of rows in the departments table.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM departments;
-- Show the number of rows in the departments table that
-- have 'en' as a substring of the dept_name value.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM departments WHERE dept_name LIKE '%en%';
-- A JOIN of information from multiple tables: the titles table shows
-- who had what job titles, by their employee numbers, from what
-- date to what date. Retrieve this information, but instead of the
-- employee number, use the employee number as a cross-reference to
-- the employees table to get each employee's first and last name
-- instead. (And only get 10 rows.)
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name,
titles.title, titles.from_date, titles.to_date
FROM titles INNER JOIN employees ON
employees.emp_no = titles.emp_no LIMIT 10;
-- List all the tables in all the databases. Implementations typically provide
-- their own shortcut command to do this with the database currently in use.
SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
WHERE TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE';
-- Sub Query
SELECT DISTINCT course_id
FROM section
WHERE semester = ‘Fall’ AND year= 2009 AND course_id IN (
SELECT course_id
FROM section
WHERE semester = ‘Spring’ AND year= 2010
);
联合查询
在一个查询输出中把两个表连接在一起。第三行很重要,因为它显示了这两个表的关系(在本例中是它们的键值)。
SELECT customers.id, customers.name, items.name, customers.state
FROM customers, items
WHERE customers.id=seller_id
ORDER BY customers.id
取 “LEFT “或 “RIGHT “左边的表(本例中为 customers),并加入它,不管它是否有任何值。所以上面的语句显示了所有的用户/客户,即使他们没有销售任何东西。
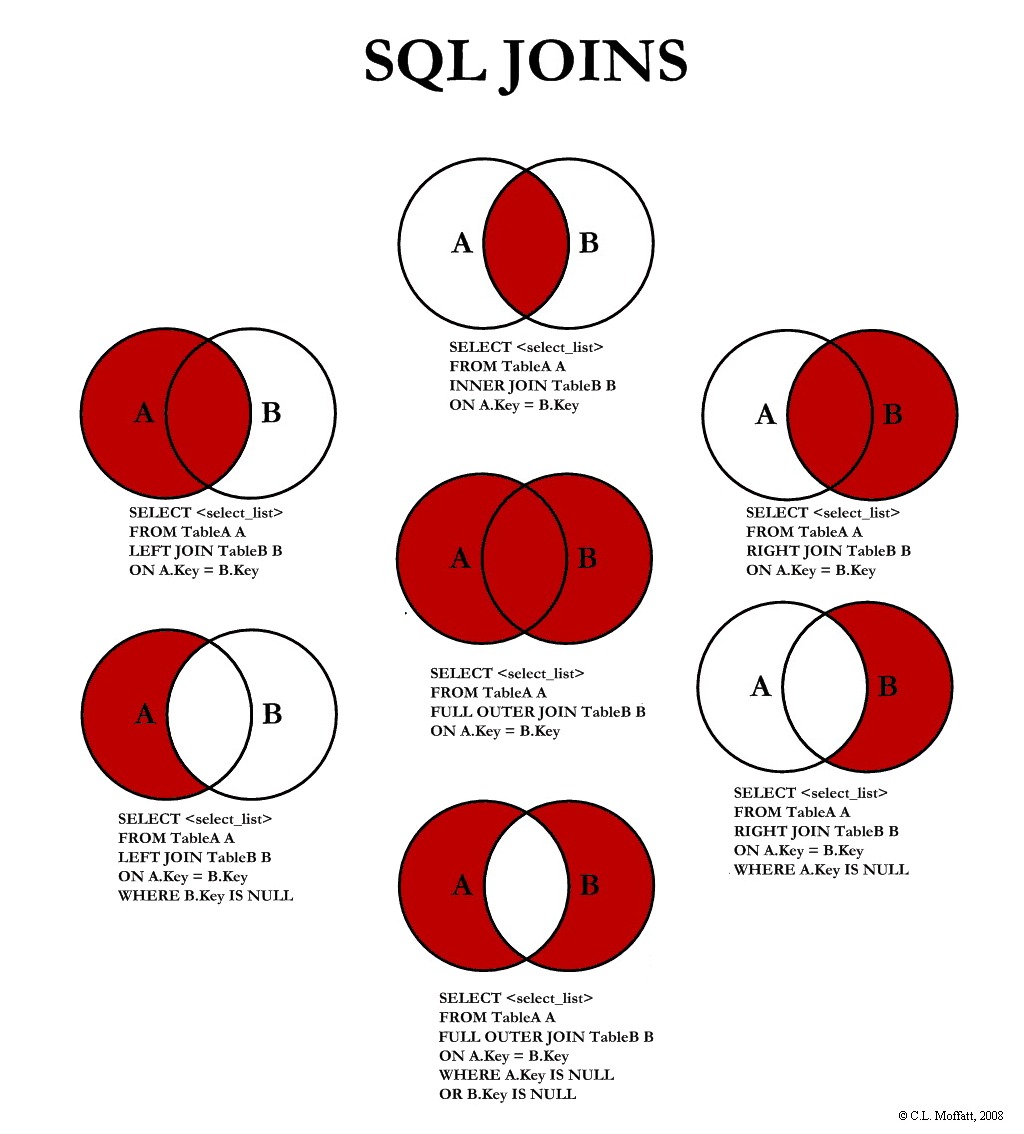
-- Having and without join
select i.dt_name, count(s.dt_stueck_titel) from tbl_stueck as s, tkey_interpret as i
where s.fi_interpret = i.id_interpret
group by i.dt_name
having count(s.dt_stueck_titel) >10
order by count(s.dt_stueck_titel) de
-- Join the hard way Inner Join
select s.dt_stueck_titel, i.dt_name
from tbl_stueck as s, tkey_interpret as i
where s.fi_interpret = i.id_interpret
order by s.dt_stueck_titel
-- Multi Join
select sa.id_jahr, st.dt_stueck_titel, ip.dt_name
from tbl_stueck as st, tass_stueck_sampler as ss, tkey_sampler as sa, tkey_interpret as ip
where ss.id_fi_stueck_nr = st.id_stueck_nr
and ss.id_fi_jahr = sa.id_jahr
and st.fi_interpret = ip.id_interpret
order by st.dt_stueck_titel
-- Join the right way Inner Equi Key Joining
select dt_stueck_titel, dt_name
from tbl_stueck join tkey_interpret
on fi_interpret = id_interpret
order by dt_stueck_titel
-- Multi Inner Equi Key Joining
select id_fi_jahr, dt_stueck_titel, dt_name
from tbl_stueck
join tass_stueck_sampler on id_fi_stueck_nr = id_stueck_nr
join tkey_interpret on fi_interpret = id_interpret
order by dt_stueck_titel
子查询
-- Select with Subqueries Select max and min values
select dt_stueck_titel as Titel, dt_zeit as Zeit
from tbl_stueck
where dt_zeit = (select max(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)
or dt_zeit = (select min(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)
order by dt_zeit;
-- Select with query in condition
select dt_stueck_titel as Titel, dt_zeit as Zeit
from tbl_stueck
where dt_zeit between (select avg(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)*0.9
and (select avg(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)*1.1
order by dt_zeit;
-- Select query as value
select dt_stueck_titel as Titel,
dt_zeit/(select avg(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)*100 as Zeit
from tbl_stueck
where dt_stueck_titel = 'You Shook Me'
-- Union Unify two result sets with a condition
select * from
(select dt_stueck_titel as titel, 'stück' as 'type' from tbl_stueck
union
select dt_name as titel, 'inter' as 'type' from tkey_interpret
union
select dt_stao as titel, 'stao' as 'type' from tkey_standort) as t
where t.titel like '%boy%'
插入与更新
-- Selected fields
INSERT INTO tkey_moral (id_moral_nr, moral_bez) VALUES (1, 'gut'), (2, 'schlecht'), (3, 'schlecht');
-- All fields
INSERT INTO tbl_kunde VALUES (3838,1,'Meier','Laura','Waldibrücke')
INSERT INTO users (first_name, last_name, email, password, location, dept, is_admin, register_date) values ('Fred', 'Smith', 'fred@gmail.com', '123456', 'New York', 'design', 0, now()), ('Sara', 'Watson', 'sara@gmail.com', '123456', 'New York', 'design', 0, now()),('Will', 'Jackson', 'will@yahoo.com', '123456', 'Rhode Island', 'development', 1, now()),('Paula', 'Johnson', 'paula@yahoo.com', '123456', 'Massachusetts', 'sales', 0, now()),('Tom', 'Spears', 'tom@yahoo.com', '123456', 'Massachusetts', 'sales', 0, now());
-- Update by conditions
UPDATE tbl_kunde SET NAME = 'Menzer' WHERE NAME = 'Waltenspühl-Menzer'
UPDATE tass_police SET praem_stufe = 101 WHERE praem_stufe = 108
-- Delete
delete from tbl_kunde
delete from tkey_moral where id_moral_nr = 4
delete from tbl_kunde where vorname = 'Peter' and name = 'Fischer' or vorname = 'Martin' and name = 'Müller'
MySQL
数据库管理
| Name | Command |
|---|---|
| mysql connect | mysql -u$username -p$password -P$port -h$dbhost $dbname |
| database encoding | set names utf8; |
| List databases | show databases; |
| List tables for current db | show tables; |
| Check table definition | describe $tablename; |
| Run sql in non-interactive way | =mysql -uUSER -pPASSWORD databasename -e “select * from t limit 10”= |
| Import db | mysql -uUSER -pPASSWORD dbname < backup.sql |
| export db | mysqldump -uUSER -pPASSWORD DATABASE > backup.sql |
| export db without schema | mysqldump -uUSER -pPASSWORD DATABASE --no-data=true --add-drop-table=false > backup.sql |
| Grant access | =GRANT SUPER ON DBNAME.user TO ‘DBUSER’@’%’= |
| Add column | ALTER TABLE expenses ADD COLUMN createtime timestamp not null default now(); |
| Delete Column | ALTER TABLE expenses DROP COLUMN createtime; |
| Delete index | DROP INDEX indexname ON table_name; |
| Create index | create index idindex on table_name(col_name) using btree; |
| Reset password | UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘MyNewPass’) WHERE User=’root’; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; |
drop user 'braindenny'@'%'; flush privileges; CREATE USER... |
|
CREATE USER 'myuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'MYPASSWORD'; |
|
| mysql8 grant privileges to user | GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON mydbname.* TO 'myuser'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION; |
$ mysql -u root -p
-- Show Users
SELECT User, Host FROM mysql.user;
-- Create User
CREATE USER 'someuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'somepassword';
-- Grant All Priveleges On All Databases
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO 'someuser'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
-- Show Grants
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'someuser'@'localhost';
-- Remove Grants
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES, GRANT OPTION FROM 'someuser'@'localhost';
-- Delete User
DROP USER 'someuser'@'localhost';
时间与日期
-- 今天
select * from 表名 where to_days(时间字段名) = to_days(now());
-- 昨天
SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE TO_DAYS(NOW()) - TO_DAYS(时间字段名) <= 1
-- 7天
SELECT * FROM 表名 where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(), INTERVAL 7 DAY) <= date(时间字段名)
-- 近30天
SELECT * FROM 表名 where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(), INTERVAL 30 DAY) <= date(时间字段名)
-- 本月
SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE DATE_FORMAT( 时间字段名, '%Y%m' ) = DATE_FORMAT( CURDATE( ), '%Y%m' )
-- 上一月
SELECT * FROM 表名 WHERE PERIOD_DIFF( date_format( now( ), '%Y%m' ), date_format( 时间字段名, '%Y%m' ) ) =1
-- 查询本季度数据
select * from `ht_invoice_information` where QUARTER(create_date)=QUARTER(now());
-- 查询上季度数据
select * from `ht_invoice_information` where QUARTER(create_date)=QUARTER(DATE_SUB(now(),interval 1 QUARTER));
-- 查询本年数据
select * from `ht_invoice_information` where YEAR(create_date)=YEAR(NOW());
-- 查询上年数据
select * from `ht_invoice_information` where year(create_date)=year(date_sub(now(),interval 1 year));
-- 查询当前这周的数据
SELECT name, submittime FROM enterprise WHERE YEARWEEK(date_format(submittime,'%Y-%m-%d')) = YEARWEEK(now());
-- 查询上周的数据
SELECT name, submittime FROM enterprise WHERE YEARWEEK(date_format(submittime,'%Y-%m-%d')) = YEARWEEK(now())-1;
-- 查询当前月份的数据
select name, submittime from enterprise where date_format(submittime,'%Y-%m')=date_format(now(),'%Y-%m')
-- 查询距离当前现在6个月的数据
select name, submittime from enterprise where submittime between date_sub(now(),interval 6 month) and now();
-- 查询上个月的数据
select name, submittime from enterprise where date_format(submittime,'%Y-%m')=date_format(DATE_SUB(curdate(), INTERVAL 1 MONTH),'%Y-%m')
Links
- 2022-Next Level Database Techniques For Developers
