Flutter-CheatSheet
📌 本文很多内容源于 Flutter 官方文档。本文主要是对于应用开发中常见的考虑进行汇总。
Flutter CheatSheet
谷歌的 Flutter 为开发人员提供了一种构建 Android 和 iOS 原生用户界面的方法,Flutter 在 Rlease 模式下直接将 Dart 编译成本地机器码,避免了代码解释运行的性能消耗。
Dart 本身针对高频率循环刷新(如屏幕每秒 60 帧)在内存层面进行了优化,使得 Dart 运行时在屏幕绘制实现如鱼得水。Flutter 实现了自己的图形绘制避免了 Native 桥接。
Technical Overview | 架构概览
Flutter has a functional-reactive framework that is inspired by React. Though Flutter is written in Dart, it also takes the best features of React and helps the developers build a beautiful, cross-platform mobile app.
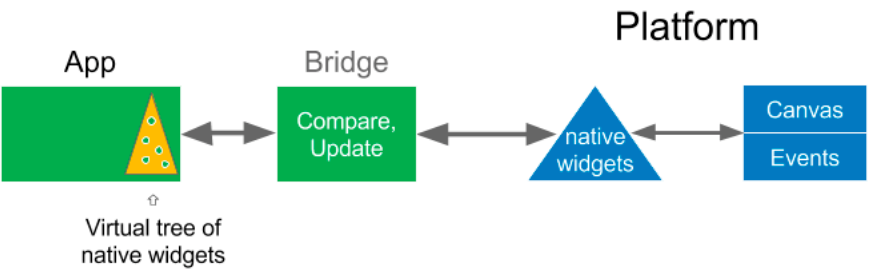
Everything’s a Widget. Widgets are the basic building blocks of a Flutter app’s user interface. Each widget is an immutable declaration of part of the user interface. Unlike other frameworks that separate views, view controllers, layouts, and other properties, Flutter has a consistent, unified object model: the widget.

Composition > inheritance. Widgets form a hierarchy based on composition. Each widget nests inside, and inherits properties from, its parent. There is no separate “application” object. Instead, the root widget serves this role. You can respond to events, like user interaction, by telling the framework to replace a widget in the hierarchy with another widget. The framework then compares the new and old widgets and efficiently updates the user interface.
You can also control the layout of a widget by composing it with other widgets. For example, to center a widget, you wrap it in a Center widget. There are widgets for padding, alignment, row, columns, and grids. These layout widgets do not have a visual representation of their own. Instead, their sole purpose is to control some aspect of another widget’s layout. To understand why a widget renders in a certain way, it’s often helpful to inspect the neighboring widgets. The Flutter framework is organized into a series of layers, with each layer building upon the previous layer.

The goal of this design is to help you do more with less code. For example, the Material layer is built by composing basic widgets from the widgets layer, and the widgets layer itself is built by orchestrating lower-level objects from the rendering layer.
If the unique characteristics of a widget need to change based on user interaction or other factors, that widget is stateful. For example, if a widget has a counter that increments whenever the user taps a button, the value of the counter is the state for that widget. When that value changes, the widget needs to be rebuilt to update the UI. Whenever you mutate a State object (e.g., increment the counter), you must call setState() to signal the framework to update the user interface by calling the State’s build method again. Having separate state and widget objects lets other widgets treat stateless and stateful widgets in the same way, without being concerned about losing state. Rather than needing to hold on to a child to preserve its state, the parent is free to create a new instance of the child without losing the child’s persistent state. The framework does all the work of finding and reusing existing state objects when appropriate.
入门开发
开发环境配置与 VSCode 配置。在 VSCode 中直接右击运行 lib/main.dart 即可以在模拟器中打开,并且进入调试模式。
# 创建新项目
$ flutter create minimal
# 打开 iOS 模拟器
$ open -a Simulator
# 运行当前应用程序
$ flutter run
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(new MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
title: 'Welcome to Flutter',
home: new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text('Welcome to Flutter'),
),
body: new Center(
child: new Text('Hello World'),
),
),
);
}
}
如果需要引入第三方依赖,首先需要在 pubspec.yaml 文件中添加依赖项声明;在 VSCode 中其会自动进行包下载,或者使用 flutter packages get 进行手动抓取。
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
cupertino_icons: ^0.1.0
english_words: ^3.1.0
在需要使用的地方导入所需要的包体,
import 'package:english_words/english_words.dart';
...
// 创建随机字符串
final wordPair = new WordPair.random();
....
// 创建新的 Text 控件
body: new Center(
//child: new Text('Hello World'), // Replace the highlighted text...
child: new Text(wordPair.asPascalCase), // With this highlighted text.
),
Flutter 将控件分为无状态控件与状态控件两大类,这里我们以简单的计数器为例,实现状态控件。所谓的状态控件,即包含了状态对象,该状态对象往往由 createState 方法构造;另外需要注意的是,对于状态控件中的不可变数据,最好声明为 final。
class CountPage extends StatefulWidget {
CountPage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
_CountPageState createState() => new _CountPageState();
}
这里的 _CountPageState 是包含了状态数据的对象,Flutter 同样允许使用 setState 方法来执行状态变更,其允许传入包含状态操作的回调函数。
class _CountPageState extends State<CountPage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {...}
}
对于值的引用允许使用占位符访问变量:
new Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.display1,
),
可以使用将响应函数绑定到内置的手势事件中:
floatingActionButton: new FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: new Icon(Icons.add),
),
Widgets
Style | 样式
Interaction | 交互
State Management | 状态管理
setState 采用了类似于 immer 这样基于 Proxy 的响应式监听模式,
